Kota Paling Berpolusi di India
Kota Paling Sedikit Terpolusi di India
Eksposur Perbandingan dengan New Delhi
24 hrs avg AQI
Polutan Udara Utama di New Delhi
PM2.5 16X
Konsentrasi PM2.5 saat ini dalam New Delhi adalah 16 times above batas yang direkomendasikan yang diberikan oleh nilai pedoman kualitas udara 24 jam WHO.
New Delhi - Lokasi Tingkat Polusi Udara
| LOKASI | Status | AQI-US | AQI-IN | PM2.5 | PM10 | Temp | Humid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITI Shahdra | POOR | 200 | 323 | 150 | 304 | 25 | 35 |
| Loni | SEVERE | 324 | 416 | 267 | 443 | 26 | 32 |
| Pooth Khurd | SEVERE | 304 | 403 | 254 | 406 | 26 | 31 |
| Ihbas | UNHEALTHY | 268 | 375 | 218 | 374 | 26 | 32 |
| ITI Jahangirpuri | HAZARDOUS | 442 | 545 | 334 | 546 | 27 | 34 |
| Narela | SEVERE | 322 | 415 | 256 | 442 | 27 | 31 |
| Mother Dairy Plant | UNHEALTHY | 260 | 369 | 210 | 361 | 26 | 32 |
| Sonia Vihar Water Treatment Plant Djb | HAZARDOUS | 412 | 508 | 306 | 516 | 26 | 32 |
| Alipur | SEVERE | 319 | 412 | 266 | 439 | 27 | 31 |
| Punjabi Bagh | SEVERE | 304 | 403 | 254 | 420 | 26 | 32 |
| Sri Auribindo Margta | SEVERE | 311 | 408 | 261 | 378 | 25 | 34 |
| Shaheed Sukhdev College Of Business Studies | HAZARDOUS | 410 | 505 | 305 | 514 | 27 | 31 |
| Delhi Institute Of Tool Engineering | HAZARDOUS | 442 | 545 | 334 | 546 | 27 | 34 |
| Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium | SEVERE | 326 | 420 | 276 | 391 | 25 | 34 |
| Satyawati College | UNHEALTHY | 292 | 394 | 242 | 372 | 26 | 32 |
| Mandir Marg | UNHEALTHY | 267 | 375 | 217 | 351 | 25 | 33 |
| Mundka | HAZARDOUS | 466 | 575 | 344 | 570 | 28 | 32 |
| RK Puram | UNHEALTHY | 263 | 372 | 213 | 360 | 25 | 33 |
| Pusa | SEVERE | 325 | 419 | 275 | 430 | 26 | 31 |
| Anand Vihar | HAZARDOUS | 438 | 540 | 279 | 542 | 27 | 34 |
| PGDAV College | UNHEALTHY | 290 | 392 | 240 | 408 | 25 | 34 |
| New Delhi Us Embassy | UNHEALTHY | 257 | 367 | 207 | 306 | 25 | 33 |
| Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium | UNHEALTHY | 239 | 353 | 189 | 316 | 26 | 32 |
| Lajpat Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 273 | 379 | 223 | 353 | 26 | 54 |
| Prashant Vihar | HAZARDOUS | 404 | 498 | 308 | 508 | 28 | 32 |
| Saket Block C | UNHEALTHY | 270 | 377 | 220 | 346 | 27 | 34 |
| Embassy of Belgium | UNHEALTHY | 273 | 379 | 223 | 349 | 26 | 54 |
| LIC Colony | SEVERE | 362 | 455 | 287 | 474 | 28 | 32 |
| Sir Edmund Hillary Marg | UNHEALTHY | 257 | 367 | 207 | 335 | 27 | 34 |
| Shastri Nagar | SEVERE | 320 | 415 | 270 | 427 | 27 | 34 |
| Uttam Nagar | SEVERE | 321 | 416 | 271 | 381 | 28 | 32 |
| Ashok Vihar Phase 1 | SEVERE | 318 | 414 | 268 | 426 | 28 | 32 |
| Rohini Sector 7 | SEVERE | 391 | 484 | 300 | 497 | 28 | 32 |
| Hari Nagar | SEVERE | 307 | 405 | 257 | 404 | 28 | 32 |
| Vasundhara Enclave | UNHEALTHY | 258 | 365 | 205 | 395 | 27 | 35 |
| Golf Links | UNHEALTHY | 268 | 375 | 218 | 335 | 27 | 34 |
| Punjabi Bagh Block D | SEVERE | 321 | 414 | 266 | 441 | 28 | 32 |
| Anand Lok | UNHEALTHY | 284 | 388 | 234 | 365 | 27 | 34 |
| Ashok Vihar Phase 3 | UNHEALTHY | 297 | 398 | 247 | 388 | 27 | 34 |
| Green Park | UNHEALTHY | 262 | 371 | 212 | 340 | 27 | 34 |
| Defence Colony | UNHEALTHY | 284 | 388 | 234 | 365 | 27 | 34 |
| Karol Bagh | UNHEALTHY | 291 | 393 | 241 | 383 | 27 | 34 |
| Kalkaji | UNHEALTHY | 276 | 382 | 226 | 384 | 27 | 35 |
| HT House | UNHEALTHY | 244 | 357 | 194 | 308 | 27 | 34 |
| Okhla Phase II | UNHEALTHY | 271 | 378 | 221 | 376 | 27 | 35 |
| Katwaria Sarai | UNHEALTHY | 269 | 376 | 219 | 337 | 27 | 34 |
| Ramesh Park | UNHEALTHY | 252 | 363 | 202 | 328 | 27 | 35 |
| Chanakya Puri | UNHEALTHY | 253 | 364 | 203 | 331 | 27 | 34 |
| Rohini Sector 30 | SEVERE | 330 | 423 | 272 | 448 | 28 | 32 |
| Anand Parbat | UNHEALTHY | 299 | 399 | 249 | 392 | 27 | 34 |
| Kohat Enclave | SEVERE | 384 | 476 | 298 | 491 | 28 | 32 |
| Greater Kailash II | UNHEALTHY | 265 | 373 | 215 | 364 | 27 | 35 |
| Mori Gate | UNHEALTHY | 253 | 364 | 203 | 315 | 27 | 34 |
| Shalimar Bagh | SEVERE | 350 | 443 | 285 | 464 | 28 | 32 |
| Panchsheel Vihar | UNHEALTHY | 262 | 371 | 212 | 340 | 27 | 34 |
| Mukherjee Nagar | SEVERE | 302 | 402 | 252 | 404 | 27 | 34 |
| Rohini Sector 24 | SEVERE | 347 | 440 | 277 | 462 | 28 | 32 |
| Dwarka Sector 10 | SEVERE | 316 | 412 | 266 | 351 | 28 | 32 |
| Model Town | SEVERE | 312 | 409 | 262 | 419 | 27 | 34 |
| Ghazipur | UNHEALTHY | 281 | 376 | 219 | 411 | 26 | 54 |
| Rohini Sector 15 | SEVERE | 371 | 464 | 289 | 481 | 28 | 32 |
| Ashok Vihar Phase 4 | UNHEALTHY | 289 | 392 | 239 | 375 | 28 | 32 |
| Janakpuri | SEVERE | 308 | 406 | 258 | 399 | 28 | 32 |
| Shahdara | UNHEALTHY | 230 | 346 | 180 | 318 | 27 | 34 |
| Wazirpur | SEVERE | 339 | 431 | 281 | 455 | 28 | 32 |
| Malviya Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 271 | 378 | 221 | 336 | 27 | 34 |
| Rajinder Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 282 | 386 | 232 | 369 | 26 | 54 |
| GTB Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 224 | 342 | 174 | 315 | 27 | 34 |
| Raghubir Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 296 | 397 | 246 | 401 | 28 | 32 |
| Civil Lines | UNHEALTHY | 256 | 366 | 206 | 318 | 27 | 34 |
| New Friends Colony | UNHEALTHY | 268 | 375 | 218 | 370 | 26 | 54 |
| Sheikh Sarai | UNHEALTHY | 261 | 370 | 211 | 332 | 27 | 34 |
| Naraina Industrial Area | UNHEALTHY | 296 | 397 | 246 | 391 | 28 | 32 |
| Inderlok | UNHEALTHY | 290 | 392 | 240 | 378 | 27 | 34 |
| Jangpura | UNHEALTHY | 281 | 385 | 231 | 346 | 27 | 34 |
| Vasant Kunj | UNHEALTHY | 271 | 378 | 221 | 335 | 27 | 34 |
| Dwarka Sector 11 | SEVERE | 314 | 411 | 264 | 342 | 28 | 32 |
| Greater Kailash | UNHEALTHY | 259 | 368 | 209 | 355 | 27 | 35 |
| Ashok Vihar Phase 2 | SEVERE | 317 | 413 | 267 | 426 | 28 | 32 |
| Hastsal | SEVERE | 308 | 406 | 258 | 397 | 28 | 32 |
| Delhi Cantt | UNHEALTHY | 253 | 364 | 203 | 331 | 27 | 34 |
| Diplomatic Enclave | UNHEALTHY | 250 | 362 | 200 | 321 | 27 | 34 |
| Bawana Industrial Area | UNHEALTHY | 298 | 398 | 248 | 410 | 28 | 32 |
| Gulmohar Park Block B | UNHEALTHY | 258 | 368 | 208 | 329 | 27 | 34 |
| Hauz Khas | UNHEALTHY | 253 | 364 | 203 | 318 | 27 | 34 |
| I P Extension | UNHEALTHY | 289 | 383 | 224 | 416 | 27 | 35 |
| Niti Marg | UNHEALTHY | 250 | 362 | 200 | 321 | 27 | 34 |
| Bali Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 292 | 394 | 242 | 400 | 28 | 32 |
| Sukhdev Vihar | UNHEALTHY | 261 | 370 | 211 | 358 | 27 | 35 |
| Delhi Gymkhana Club | UNHEALTHY | 241 | 355 | 191 | 308 | 27 | 34 |
| Paschim Vihar | UNHEALTHY | 292 | 394 | 242 | 400 | 28 | 32 |
| Dwarka Sector 6 | SEVERE | 313 | 410 | 263 | 351 | 28 | 32 |
| Saket | UNHEALTHY | 257 | 367 | 207 | 324 | 27 | 34 |
| Dwarka Sector 23 | SEVERE | 303 | 402 | 253 | 318 | 28 | 32 |
| Safdarjung Enclave | UNHEALTHY | 250 | 362 | 200 | 326 | 27 | 34 |
| Darya Ganj | UNHEALTHY | 241 | 355 | 191 | 298 | 27 | 34 |
| Deepali | SEVERE | 335 | 428 | 274 | 452 | 28 | 32 |
| Dwarka Sector 12 | SEVERE | 313 | 410 | 263 | 351 | 28 | 32 |
| Dwarka Sector 7 | SEVERE | 302 | 402 | 252 | 321 | 28 | 32 |
| Bhalswa Landfill | SEVERE | 360 | 453 | 288 | 472 | 27 | 34 |
| Dwarka Sector 5 | UNHEALTHY | 297 | 398 | 247 | 324 | 28 | 32 |
| Dwarka Sector 18B | SEVERE | 312 | 409 | 262 | 351 | 28 | 32 |
| Dwarka Sector 3 | SEVERE | 307 | 405 | 257 | 346 | 28 | 32 |
| Mayur Vihar | UNHEALTHY | 250 | 362 | 200 | 370 | 27 | 35 |
| Vasant Vihar | UNHEALTHY | 248 | 360 | 198 | 325 | 27 | 34 |
| Sukhdev Vihar DDA Flats | UNHEALTHY | 256 | 366 | 206 | 350 | 27 | 35 |
| Kashmiri Gate ISBT | UNHEALTHY | 256 | 366 | 206 | 322 | 27 | 34 |
| New Sarup Nagar | SEVERE | 395 | 488 | 304 | 500 | 27 | 34 |
| Mustafabad | UNHEALTHY | 273 | 379 | 223 | 383 | 27 | 34 |
| Siddhartha Enclave | UNHEALTHY | 268 | 375 | 218 | 356 | 26 | 54 |
| Hazrat Nizamuddin | UNHEALTHY | 280 | 385 | 230 | 339 | 27 | 34 |
| Connaught Place | UNHEALTHY | 237 | 352 | 187 | 294 | 27 | 34 |
| East Patel Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 289 | 392 | 239 | 377 | 26 | 54 |
| Saraswati Marg | SEVERE | 352 | 445 | 279 | 466 | 28 | 32 |
| Loni Dehat | SEVERE | 302 | 402 | 252 | 425 | 27 | 34 |
| Surya Nagar | UNHEALTHY | 240 | 354 | 190 | 368 | 27 | 34 |
| Rohini Sector 10 | SEVERE | 349 | 441 | 276 | 463 | 28 | 32 |
| Rohini Sector 5 | SEVERE | 334 | 426 | 271 | 451 | 28 | 32 |
| RK Puram North Block | UNHEALTHY | 244 | 357 | 194 | 320 | 26 | 54 |
Kondisi Cuaca di New Delhi
Waktu lokal
Wind speed
33 km/h
UV Index
16
Pressure
800 mb
Saran Kesehatan Untuk New Delhi
Pakai Masker
Tetap di dalam ruangan
jendela
Gunakan Pemurni
Keluarga
New Delhi Prakiraan Kualitas Udara
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
New Delhi
AQI Kalender
Most Polluted Cities in India
Least Polluted Cities in India
Comparative Exposure with New Delhi
24 hrs avg AQI
FAQ dari New Delhi Indeks Kualitas Udara
(Pertanyaan yang Sering Diajukan)
Jawaban cepat untuk beberapa pertanyaan umum tentang polusi udara New Delhi.
Kualitas udara waktu nyata di New Delhi adalah 400 (UNHEALTHY) AQI sekarang. Ini terakhir diperbarui 3 minutes ago .
Konsentrasi PM2.5 saat ini dalam New Delhi adalah 240 (µg/m³). Organisasi Kesehatan Dunia (WHO) merekomendasikan 15 µg/m³ sebagai konsentrasi ambang batas PM2.5 selama 24 jam rata-rata. Saat ini, konsentrasinya adalah 9.60 kali batas yang disarankan.
Secara umum kualitas udara pada New Delhi mulai memburuk pada akhir Oktober. Musim dingin adalah musim yang paling parah terkena polusi udara.
Anda harus memakai masker N95 yang baik saat Anda pergi ke luar ruangan New Delhi sampai AQI membaik hingga kisaran sedang.
Orang yang pergi ke kantor harus menghindari kendaraan pribadi dan menggunakan transportasi umum atau carpooling.
(i) Penyebab utama polusi udara luar ruangan adalah partikel padat dan cair yang disebut aerosol & gas dari emisi kendaraan, aktivitas konstruksi, pabrik, pembakaran jerami & bahan bakar fosil, dan kebakaran hutan, dll.
(ii) Penyebab utama polusi udara dalam ruangan adalah gas berbahaya dari bahan bakar memasak (seperti kayu, limbah tanaman, arang, batu bara dan kotoran), lembab, asap jamur, bahan kimia dari bahan pembersih, dll.
Polusi udara dalam ruangan di New Delhi sama berbahayanya dengan polusi luar ruangan, karena polusi udara masuk ke dalam rumah atau bangunan melalui pintu, jendela dan ventilasi.
Di New Delhi , Anda harus menggunakan pembersih udara atau mesin udara segar di rumah atau kantor dalam ruangan dan menutup semua pintu, jendela dan ventilasi ketika indeks kualitas udara luar (aqi) di New Delhi sangat tinggi. Ventilasi yang tepat sangat disarankan hanya jika kualitas udara luar ruangan membaik dan kisaran AQI sedang.
Peringkat AQI Kota & Negara Paling Berpolusi di Dunia
Kota paling tercemar secara real-time, dan peringkat AQI historis bulanan & tahunan untuk kota & negara
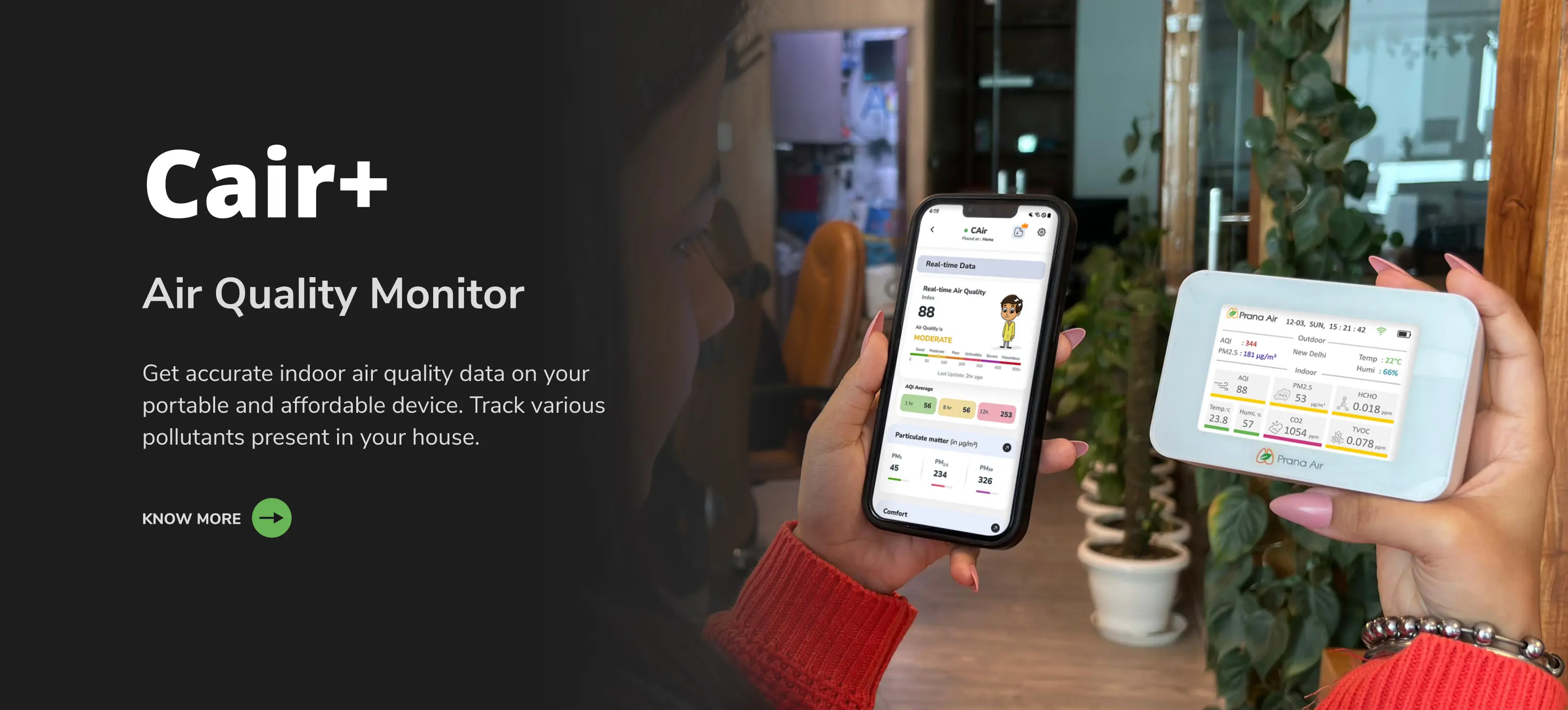
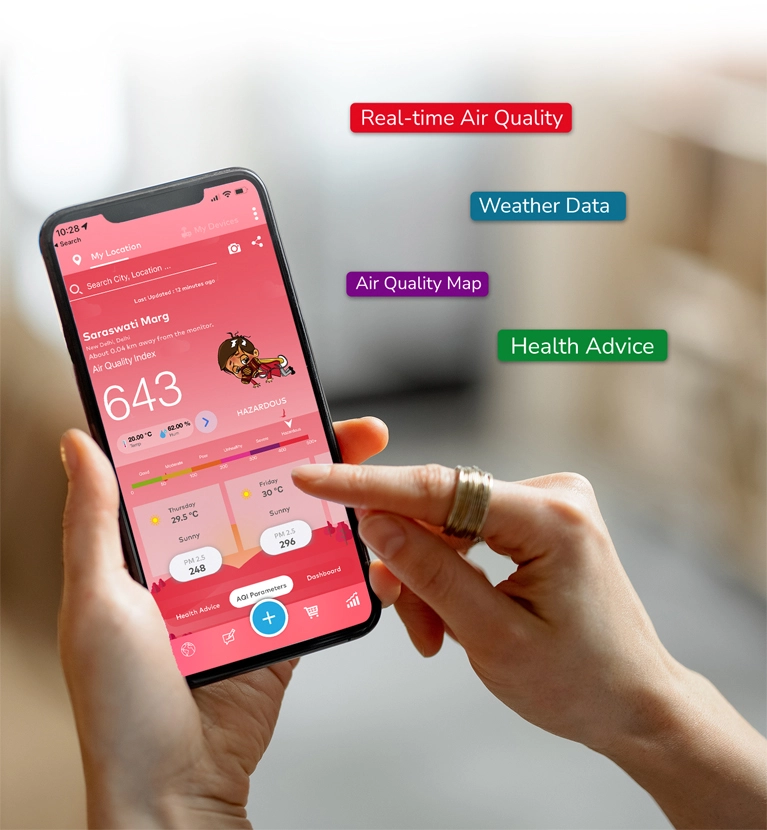
Solusi Kualitas Udara untuk New Delhi
Cari tahu pemantau & solusi kualitas udara Prana Air untuk memerangi polusi udara di kota Anda.
New Delhi POLUSI UDARA
A report by the Environmental Performance Index in 2014 said that a total decline of 100 percent was seen in the air quality of India in the last 10 years and the city that has been hit the greatest is the capital city, New Delhi, India. Research by Berkeley Earth revealed that on an average, when the AQI is in a relatively better state than the usual, breathing that air still means that pollutants equal to the same amount as 31 cigarettes smoke entering your lungs.
With statistics like these, all of us need to be educated and concerned about the rising Delhi pollution level. Learn about the causes and effects of Delhi air pollution so that we can understand the problem and try to bring a change on a personal and public level.
What are the Main Sources & Causes of Delhi Pollution?
There are many causes and sources of Delhi air pollution like stubble burning, vehicle emissions, industrial pollution, construction, cold weather, geographic location, stagnant winds, population growth, Badarpur thermal power plant, fire in Bhalswa Landfills, etc.
1. Agricultural Stubble Burning
Agricultural stubble burning has been the major caterer to the rising air pollution and smog in Delhi. The problem is that as there is a very short time gap between the harvesting of paddy and wheat, the straw from the last harvest needs to be disposed off as soon as possible. The government has suggested the farmers do manual or mechanical management of straw but as the process is expensive and takes more time, farmers switch back to their traditional practice of stubble burning. Thousands of crores have been spent by the Central and the State government of India, a ban has been put on the practice but stubble burning has not come under control yet. The smoke from this agricultural burning gets transported to Delhi because of the westerly winds. According to a study by IIT Kanpur, agricultural burning is the third largest contributor towards particulate matters in Delhi.
2. Vehicular Emissions
It is the number one contributor to the PM2.5 and PM10 particles in Delhi which is 28%. And overall, out of the total air pollution, 41 percent is due to vehicular emissions. Vehicular emissions have a large number of carbon monoxide in them. Long exposure to it can cause death and more and more vehicular emission is causing CO to accumulate in our atmosphere.
3. Industrial Pollution
Delhi has the highest number of small-scale industries in India and they do not respect any limits on the emission of toxic fumes and pollutants. They are the second highest contributor to the poor air quality of Delhi with 3182 industries.
4. Dust By Construction Pollution
Construction and dust pollution has been one of the major factors that led to this massive air pollution in Delhi. According to DPCC, 30 percent of the Pollution in Delhi has been due to the construction and demolition. This pollution is not much under attention and the government right now is taking steps to change that.
5. Fire in Bhalswa Landfills
Bhalswa Landfill is a dumping ground that has been in use since 1984. It spread about 52 acres and has reached to heights of 62 metres. It has been creating havoc in Delhi for years now. The landfill has been used beyond its capacity way before but still no waste management has been done. The waste that keeps lying around starts decomposing and because the volume of waste is so high that the whole area becomes prone to a fire. Because of the nature of the waste, the smoke from the fire not only produces a large amount of particulate matter, it also releases toxic amounts of Carbon Monoxide, Hydrogen Sulphide among the few. In 2019 also, an incident where a fire started that set the landfill and Jahangirpuri ablaze.
6. Colder Weather
Cold weather in Delhi has also managed to be a significant part of Delhi pollution. As the temperature dips in Delhi, it lowers the aversion height of all the smog and other particulate matters in the air. Aversion height is the altitude from ground towards the sky, till which the particulate matter can rise. During summers, the aversion height is much above and far from the ground so all the pollutants rise up and are not much harmful to us . But when the winters come, the aversion height drops, which leads to all the smog being a part of the air we inhale.
7. Stagnant Winds
With a huge amount of pollutants being dispersed in the Delhi air daily, stagnant winds can cause a problem. When these huge amounts of pollutants don’t get a good speed of the wind, they start accumulating at a place which causes a hazy smog and doesn’t let the pollutants spread out.
8. Geographic Location
Delhi is landlocked between the states of Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh which and Himalayas and due to this, the winds that can carry the pollutants is near to non-existent. The winds that come from the coastal region carry pollutants with them which get trapped by the Himalayas i.e. in Delhi. For example, Chennai’s vehicle density is 19 times more than Delhi’s but still Chennai has a moderate amount of particulate matter in its air because as its a coastal region and all its pollutants get carried away.
9. Population Growth
Population growth is the grass-root cause of air pollution. More people means more vehicles, more amenities, more industrial products, more agricultural practices. Delhi saw a stark population increase from 2011 to 2019. The population went from 16.7 million in 2011 to 20 million in 2019.
10. Not Enough Public Transportation
Even though Delhi boasts of managing the world’s biggest fleet of buses under it, this system needs to be bigger and better. Because as the public transport will be better and cheaper, then only there will be less vehicular emissions. Even though Delhi is 14 times bigger than Paris, Paris’s metro line is double the length of Delhi's.
11. Lack of Active monitoring
Earlier also, active monitoring wasn’t done which led to a sudden realization after years that pollutant levels in the air have shooted. Active monitoring could have helped know the rising patterns of the air pollution so that it could be curbed at its initial days.12. Badarpur Thermal Power Plant
Badarpur Thermal Power Plant has been one of the major contributors to air pollution in Delhi in the past. But in 2015, it was seen that even though its share in electricity supply in Delhi was approximately 8 percent,but its share in the total number of particulate matters in Delhi was 80-90%.It was shut down in 2015 as a measure to reduce the number of air pollutants in the air.History of Delhi Pollution: How has it been through the years?
1980s: The Start: Delhi started seeing a rise in the pollution levels in the 80’s where the emergence of vehicles started taking a toll on the air and stubble burning started in the states of Punjab and Haryana. At that time, riots were also on a high after Indira Gandhi got assassinated and banning burning of crops seemed like an anti-religion rule so all the state governments avoided rolling it out and thus the pollution started rising.
1996: The situation of the city worsened to which the Supreme Court ordered the Delhi Government to submit a plan on how they plan on reducing the rising Delhi air pollution.
1998: Increase in Diesel run vehicles peaked the amount of PM2.5 particles in the air.
2000: There was an enormous increase in a lot of pollution causing activities like construction, industrial manufacturing and vehicular emissions. From the 2000 to 2010, the level of PM10 particles in air went from moderate to poor levels. Vehicles also increased in the capital city of India with an annual growth rate of 10.75%.
2004: The National Air Quality Index was introduced seeing the air pollution scenario. Under the NAQI, air was categorized into six levels. good, satisfactory, moderate, poor, very poor and severe/hazardous to differentiate how polluted the air was.
2016: In October 2016, Delhi underwent a major smog episode, one of its first in line of the other that came through. Air Quality Index. As the Diwali season set in, the PM2.5 level in Delhi city reached approximately 750 μg/m3 to the horror of everyone. The AQI levels reached close to 13 times more than the permissible amount. This awoke Delhi and its officials and the government bodies to the devastating effects of air pollution. The whole city got covered with smog.
2017: Kabut Asap Besar di Delhi - Insiden yang dikenal sebagai kabut asap besar telah menjadi fase paling menghancurkan yang harus dilalui Delhi dalam hal polusi udara. Tingkat PM2.5 dan PM10, yang batas sehatnya adalah 60-100 μg/m3, naik menjadi 999 μg/m3 yang merupakan tingkat tertinggi yang dapat dihitung oleh sensor. Pada tahun yang sama di bulan November 2017, pada hari kedua pertandingan uji coba antara Sri Lanka dan India, 2 pemain mulai muntah karena jumlah kabut asap dan polutan yang sangat besar di udara.
2018: Konsentrasi PM2.5 meningkat dan tingkat AQI mencapai 400. Visibilitas rendah dan masalah pernapasan meningkat.
2019: Pada bulan November, keadaan darurat kesehatan masyarakat diumumkan karena kabut asap yang parah. Penutupan sekolah dan pembatasan aktivitas di luar ruangan diberlakukan. Dan tingkat AQI melebihi 500 di banyak area karena pembakaran jerami di negara bagian tetangga.
2020: Penguncian COVID-19 secara drastis mengurangi polusi udara. Namun, kebakaran hebat di lokasi TPA Bhalswa meningkatkan tingkat AQI. Dan pada bulan November AQI melonjak menjadi 435 kategori “berbahaya”.
2021: Kebakaran kembali terjadi di TPA Ghazipur pada tahun 2021 sehingga memperburuk kualitas udara. Dan pasca Diwali meningkatkan tingkat AQI menjadi 462 karena pembakaran jerami terutama di Haryana dan Punjab.
2022: Kebakaran besar di TPA Bhalswa menarik perhatian pada pengelolaan sampah dan polusi udara yang ditimbulkannya. Sekali lagi tingkat AQI mencapai 302 pada bulan November karena banyak alasan.
2023: Tingkat rata-rata tahunan PM2.5 mencapai 100,9 (µg/m3) dan meningkat 2 percent dibandingkan tahun 2022. Peningkatan berkala tercatat pada tingkat AQI, namun kualitas udara membaik dibandingkan tahun-tahun sebelumnya. Sebuah laporan kualitas udara menyatakan New Delhi sebagai ibu kota paling tercemar di dunia.
2024: Pada awal tahun, AQI tercatat memburuk karena melewati level 400. Namun untuk pertama kalinya dalam sembilan tahun terakhir, AQI di Delhi selama bulan Februari tetap kurang dari 200. Hingga April AQI tetap pada level yang lebih baik. Namun, gelombang panas dan suhu yang meningkat meningkatkan AQI ke tingkat yang tidak sehat hingga berbahaya.
What are the effects of Delhi Air Pollution?
1. Health Problems
In Delhi, poor air quality has damaged the lungs of half of the children in Delhi, according to WHO. As PM2.5 is such a small particle it can easily enter one’s lungs and erode one’s respiratory wellness.Increased risks of cancer, epilepsy and diabetes has also been seen among the children.
PM2.5 and PM10 particles are the main causes of reduced lung capacity. This in turn leads to sore throat, cough, asthma, allergies and lung cancer. Excessive CO2 in the air leads to headache, fatigue and loss of productivity. The number of non-smokers in Delhi who suffered from lung cancer shot up from 10 percent to 50 percent in a decade, all due to the increased pollutants in the air that people have to breathe.
2. Smog in the air
Smog is exactly what the name might suggest, it is the mixture of smoke and fog. Excessive pollution in air causes smog and Delhi has had its fair share of smog over the years. Delhi observed the great smog in November 2017 which engulfed the whole city in it.
3. Environment change
The environment is constantly degrading with the increasing air pollution. The main effect of Delhi pollution in the environment is the depletion of the ozone layer in the atmosphere due to which the UV rays from the Sun can directly enter the earth. The emission from industries is also a big cause for the global warming that is leading the glaciers to melt at a really fast pace.
4. Economy
Thousands of crores have been spent by the Central Government and the Punjab and Haryana Government to stop the stubble burning and help with better ways to dispose of the waste. Delhi Government has also been getting Green funds to fight the Air Pollution and curb it.
Measures taken Up By the Government to control Delhi Pollution
1988: As advised by Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA), the Court made a ruling that the buses in the city change from using Diesel to CNG.
2010: BS-IV based vehicles were said to be mandatory.
2014: Air Quality Index was launched by the Union Environment Ministry.
2016: Arvind Kejriwal’s Promises
- ● Delhi Schools to be shut while AQI levels are at hazardous levels.
- ● Construction and demolition work stopped for 5 days.
- ● Diesel generators asked to be shut for 10 days
- ● The Environment department was asked to make an applicationto monitor burning of the leaves in the city.
- ● Vacuum cleaning of roads will be done
- ● Water sprinkling will start at areas with high PM 10 levels
- ● People will be advised to stay at home
- ● Faster adoption and manufacturing of electric vehicles will be done
- ● Vehicles that are older than 15 years will be fined
- ● Smog towers will be installed at hot spots
- ● By 2021, Delhi metro will be powered 100% by solar energy.
2017: The ‘Odd-Even’ rule was imposed. Parking fees were imposed and increased but due to no proper system, this scheme failed. Crackers were banned.
2018: Rencana Tindakan Respons Bertahap (GRAP) memulai upaya untuk mengatasi polusi udara karena episode-episode parah. Seperti pembatasan aktivitas konstruksi, dan peningkatan pemantauan.
2019: Pemerintah dan GRAP kembali memperkenalkan skema pembatasan kendaraan ganjil-genap selama periode puncak polusi. Selain itu, mereka mempromosikan kendaraan listrik (EV) untuk mengendalikan polusi udara.
2020: Dibentuk tim polusi udara yang terdiri dari 10 anggota. Tugas mereka adalah memeriksa keluhan dari Aplikasi Seluler Green Delhi dan kemudian bekerja untuk menyelesaikannya. Sedikit kelegaan dalam polusi udara sehingga kampanye kesadaran publik meningkat dan pembatasan kembang api tetap berlanjut saat Diwali.
2021: Komisi Manajemen Kualitas Udara (CAQM) dibentuk untuk memerangi polusi udara. Penutup hijau meningkat di Delhi. Semua pembangkit listrik berbasis termal (batu bara) ditutup dan pembangkit listrik berbasis gas dipromosikan. Taman eco limbah elektronik pertama dibangun di Delhi dan mendesak negara-negara tetangga untuk bekerja sama mengatasi polusi udara.
2022: Pemerintah telah meningkatkan penggunaan mesin pembersih jalan yang melibatkan senjata air dll. Bus listrik pertama diluncurkan untuk meningkatkan transportasi umum dan mengurangi emisi gas alam. Setiap kendaraan yang lebih tua dari 10-15 tahun dilarang karena emisi.
2023: Ruang Perang Hijau telah didirikan untuk memantau polusi udara. Meluncurkan Aplikasi Green Delhi bagi warga untuk melaporkan polusi udara di dekat mereka secara langsung. Bio-dekomposer PUSA disemprotkan oleh pemerintah di sekitar 3.200 hektar lahan pertanian untuk mengelola pembakaran jerami.
2024: Senjata anti-kabut asap dan penyiram air digunakan untuk mengurangi polusi debu. Lebih dari 200 tim ditugaskan untuk memantau polusi di lokasi industri dan konstruksi. Penegakan PUCC (sertifikat polusi di bawah kontrol) ditingkatkan dan lebih dari 100.000 pengendara didenda hingga bulan Mei. Tim khusus dikerahkan untuk titik-titik polusi.
· · ·How bad is the infamous Delhi Pollution
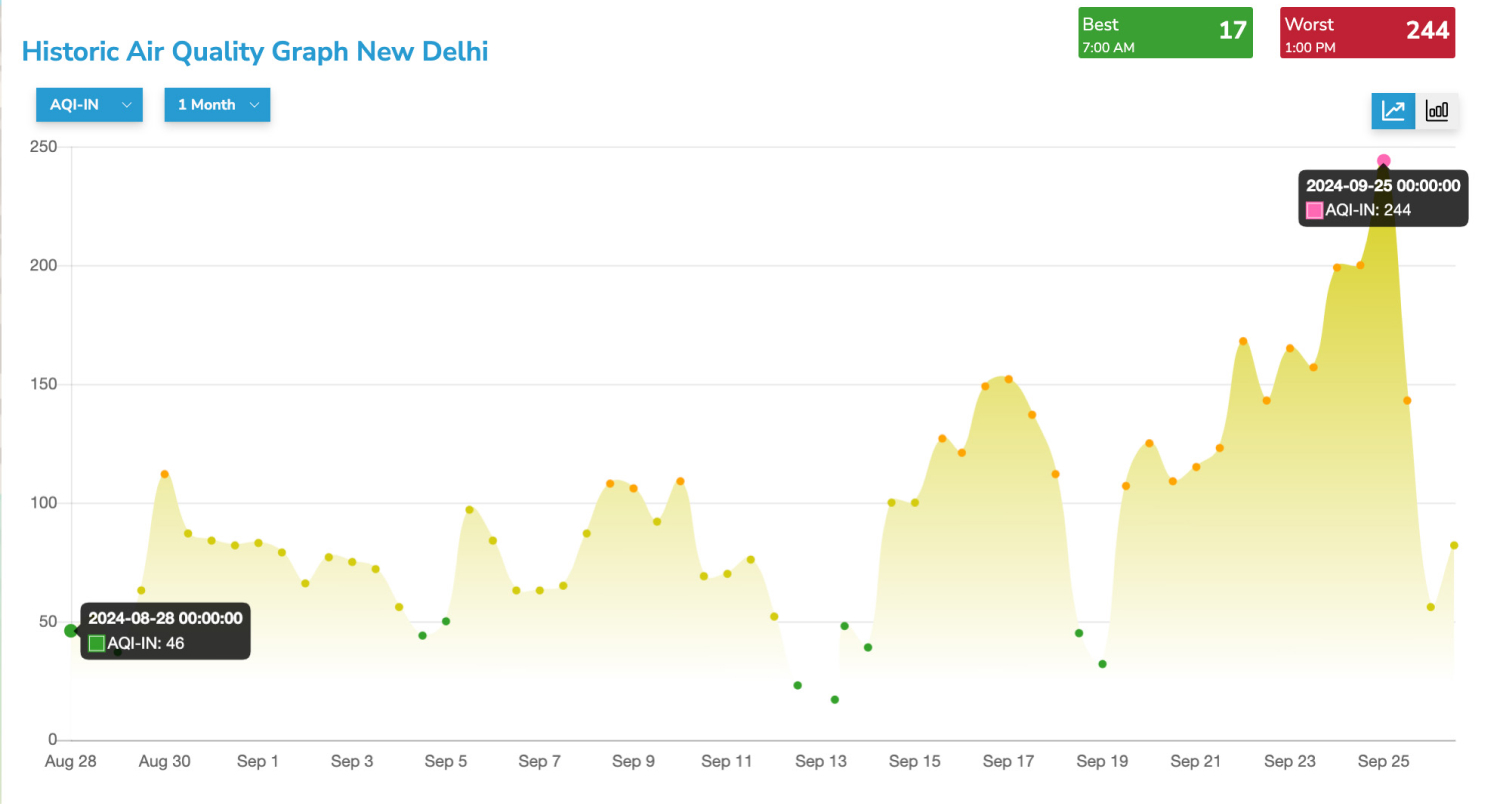
The residents of the capital city of India have to bear the brunt of the annual winter pollution. The air quality drops to such a level that the city is compared to a gas chamber! Delhi starts witnessing high levels of air pollution in late October and the contamination worsens until the end of the year. Many parts of the city experience pollution levels as high as 150 times the stipulated levels recommended by the World Health Organisation.
As a result of these events, the pollution levels are lesser in summers as compared to winters, provided the spatial and meteorological remain the same. You can observe a similar effect during winter afternoons. The increase in heat levels down pollution slightly.The early mornings and the nights are the worst. The impact of inversion is visibly evident, which is why the air quality plummets during these hours.
Why does Delhi air quality index deteriorate in winters?
Atmospheric inversion occurs in winters. The normal conditions reverse themselves, and air near the lower atmosphere is cooler and denser. The relatively warmer air of the upper layers, hence, acts as an atmospheric lid. This lid entraps the pollutants within the cold layer and evades their atmospheric dispersion. Therefore, the vertical mixing occurs in the lower layer itself.At constant emission rates and concentration of pollutants, the lesser the temperature, the more is the pollution.
As a result of these events, the pollution levels are lesser in summers as compared to winters, provided the spatial and meteorological remains the same. You can observe a similar effect during winter afternoons. The increase in heat levels down pollution slightly.The early mornings and the nights are the worst. The impact of inversion is visibly evident, which is why the air quality plummets during these hours.
However, one of the worst incidents happened during an international cricket test match between India and Sri Lanka in December 2017. The match was stopped because many Sri Lankan players became sick. Several players experienced breathing problems and vomited. The Indian Medical Association expressed their concern over the unfortunate incident and insisted ICC to adopt a policy on pollution.