Most Polluted Cities in India
Least Polluted Cities in India
Comparative Exposure with Noida
24 hrs avg AQI
Current Air Quality in Noida
PM2.5 9.7X
The current PM2.5 concentration in Noida is 9.7 times above the recommended limit given by the WHO 24 hrs air quality guidelines value.
Noida - Air Pollution Level - Locations
| LOCATIONS | Status | AQI-US | AQI-IN | PM2.5 | PM10 | Temp | Humid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Park Iii | POOR | 181 | 280 | 114 | 292 | 26 | 43 |
| Sector 1 | UNHEALTHY | 208 | 329 | 158 | 344 | 26 | 33 |
| Omicron 1A | POOR | 199 | 322 | 148 | 323 | 24 | 61 |
| Sector Omega 1 | POOR | 195 | 316 | 141 | 311 | 24 | 61 |
| D5 LOGIX INFOTECH PARK | UNHEALTHY | 220 | 338 | 170 | 359 | 27 | 35 |
Weather Conditions in Noida
Local Time
Wind speed
33 km/h
UV Index
16
Pressure
800 mb
Health Advice For Noida
Wear Mask
Stay Indoor
Windows
Use Purifier
Family
Noida Air Quality Forecast
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
134
AQI
Noida
AQI Calendar
Most Polluted Cities in India
Least Polluted Cities in India
Comparative Exposure with Noida
24 hrs avg AQI
FAQs of Noida Air Quality Index
(Frequently Asked Questions)
Quick answers to some commonly asked questions about the air pollution of Noida.
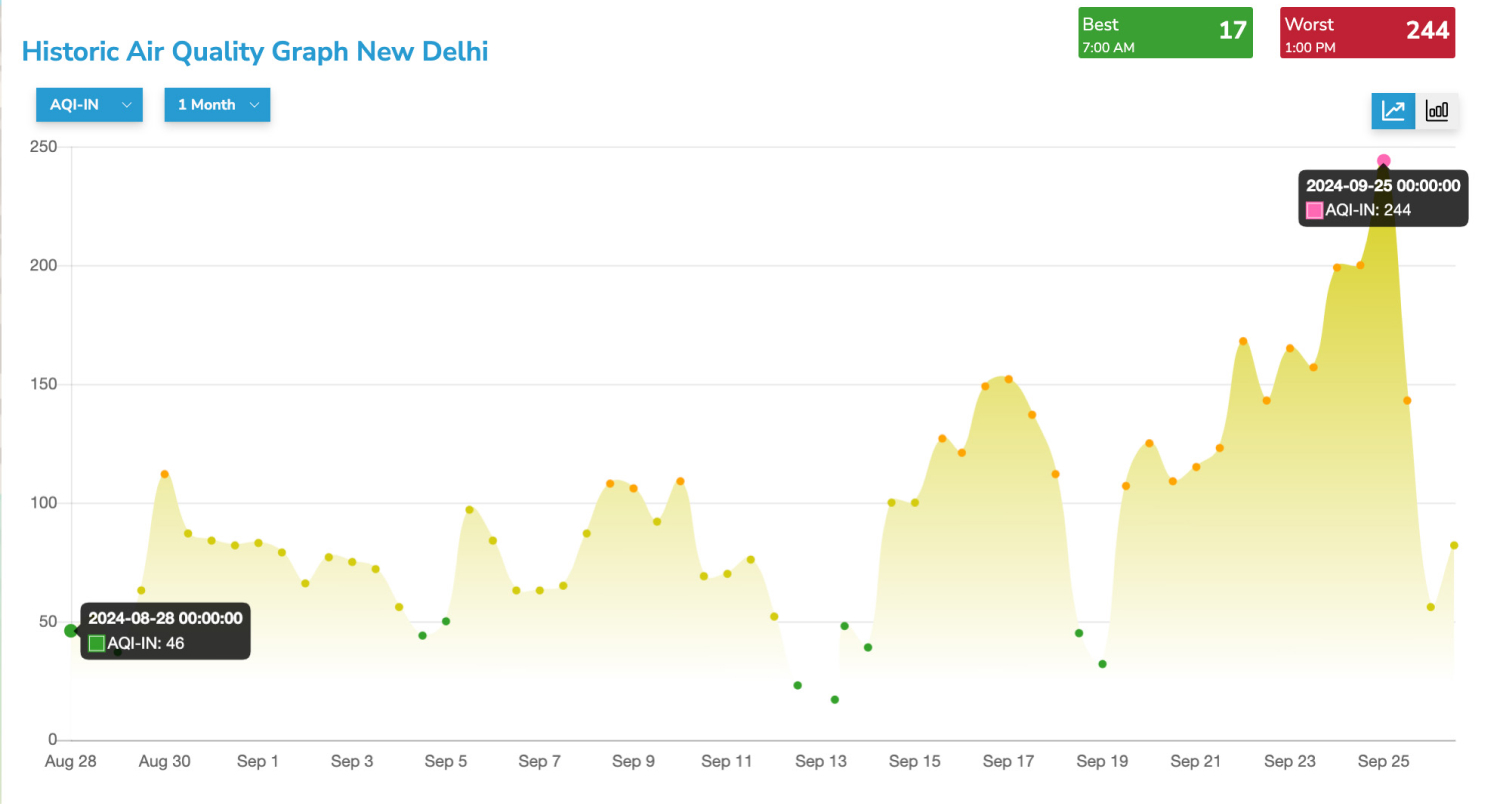
The real-time air quality in Noida is 317 (UNHEALTHY) AQI now. This was last updated 3 minutes ago .
The current concentration of PM2.5 in Noida is 146 (µg/m³). The World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends 15 µg/m³ as the threshold concentration of PM2.5 for 24 hrs mean. Currently, the concentration is 5.84 times the recommended limit.
Generally, the air quality at Noida starts deteriorating in late October. The winters are the worst-hit season in terms of air pollution.
You should wear a good N95 mask when you go outdoor in Noida until the AQI is improving upto moderate range.
Office going people should avoid personal vehicles and use public transportations or carpooling.
(i) The primary causes of outdoor air pollution are solid, liquid particles called aerosols & gase from vehicles emissions, construction activities, factories, burning stubble & fossil fuels and wildfire, etc.
(ii) Main causes of indoor air pollution are harmful gases from cooking fuels (such as wood, crop wastes, charcoal, coal and dung), damp, mould smoke, chemicals from cleaning materials, etc.
Indoor air pollution in Noida is as dangerous as outdoor pollution, because the air pollutants come inside the houses or buildings through doors, windows and ventilation.
In Noida , you must use an air purifier or fresh air machine at home or office indoor and close all the doors, windows and ventilations when the outdoor air quality index (aqi) in Noida is very high. Proper ventilation is highly recommended only when outdoor air quality is improving and moderate AQI range.
World's Most Polluted Cities & Countries AQI Ranking
Real-time top most polluted cities, and monthly & annual historic AQI ranking of cities & countries
Air Quality Solutions for Noida
Find out Prana Air's air quality monitors & solutions to fight air pollution in your city.
Noida AIR POLLUTION
Noida AIR POLLUTION
Noida is a part of the National Capital Region, India, and is located in Gautam Buddha Nagar of Uttar Pradesh. The population of Noida was 642,381 (Census of India, 2011). Considered to be one of the most polluted cities in the world, and listed in the top 10 polluting areas in the world, Noida's air pollution levels are extremely dangerous. Air Quality in Noida can sometimes be worse than in Delhi and other north Indian states.
Noida produces large amounts of air pollutants, these are:
● Emissions from Automobiles: Due to heavy traffic, the average levels of black carbon, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter (PM) found on Noida's roadways are extremely high. According to a study conducted by CPCB, the particulate concentration was ten times greater than typical levels. The study claims that 80 percent of the citizens suffer from eye or skin discomfort as a result of high concentrations of black carbon, CO, and PM. Each of the crossings sees a large number of traffic every day, with estimates ranging from 20,000 to 50,000 passenger car units each day, as estimated by the officials.
● Road dust: Noida residents claim that the concerned authorities are not performing their job of maintaining the poor conditions of roads, open spaces, and pavements that prevents dust from mixing with the air and causing air pollution. According to experts, 'Overly polluted air can harm citizens' health, particularly youngsters and the elderly.
● Construction and extraction: Dust pollution from construction activities without adequate precautions continue to choke Noida - one of the most polluted cities in Delhi-NCR, despite the graded action plan (GRAP) continuing to be in force across the city '(a report by Hindustan Times). As reported by a resident living near a construction site', during the daytime strong winds often carry soil and larger dust particles from the construction site to their houses.
● Industrial Emissions: Industrial emissions are consistent season after season. According to a research published in August 2018, industries were responsible for 22% of air pollution.
● Stubble and trash burning: Noida produces approximately 200-250 tonnes of garbage per day. If this garbage is not disposed of in the most environment - friendly manner possible, rather than burning, it might result in serious health problems among the citizens. According to experts, stubble burning accounts for at least 15-20% of the city's air pollution.
Reports, Facts, and Figures About Noida Air Quality Index
● Uttar Pradesh Pollution Control Board (UPPCB) says, dust is the major source of pollution in most NCR districts, followed by industrial emissions.
● An August 2018 report says, PM10 is the most prominent pollutant in NCR cities. In Noida, during the summer months, 47% of the PM10 in the atmosphere was because of dust, 22% was contributed by industries, 13% by vehicles, 12% by biomass, and 6% by others. During winters, 29% of the PM10 was caused by dust, 25% each by industries and vehicles, 12% by biomass, and 9% by others.
● A Bimhow research says, 'the construction sector contributes to 23% of air pollution, 50% of climatic change, 40% of water pollution, and 50% of landfill wastes.
Health Impacts due to Noida - 'very poor' PM2.5 conditions
1. Vehicle emissions aggravate asthma, impair lung capacity, and make people more vulnerable to respiratory ailments like pneumonia and bronchitis.
2. According to the study by Järlskog et al., road dust contains a large number of black particles <100 µm. These smaller MPs have a greater potential to harm human health, particularly in the cardiorespiratory system.
3. Heart disease, lung cancer, asthma, and acute lower respiratory infection are all linked to construction and demolition operations.
4. Birth defects, cancer, immune function abnormalities, kidney and liver dysfunction, lung and respiratory ailments, and neurotoxic disorders are all linked to industrial pollution.
5. Cancers, liver disorders, immune system, endocrine, and reproductive system dysfunction, as well as effects on the developing neurological system and other developmental events.
Action Plans By Uttar Pradesh Government
The Uttar Pradesh Pollution Control Board is monitoring Noida's ambient air quality and has planned to take the following initiatives for both short and long-term periods:- 1. Vehicle emission control
- 2. Suspension of road dust and other fugitive emissions control
- 3. Control of emissions from biomass/crop residue/garbage/municipal solid waste burning
- 4. Control of industrial emissions
- 5. Control of air pollution from construction and demolition activities